🌐 Webhook Trigger
The Webhook Trigger enables external systems to initiate workflows in SmartFlow by sending data via API requests. This trigger is ideal for integrating SmartFlow with third-party applications, allowing dynamic and seamless automation of tasks.
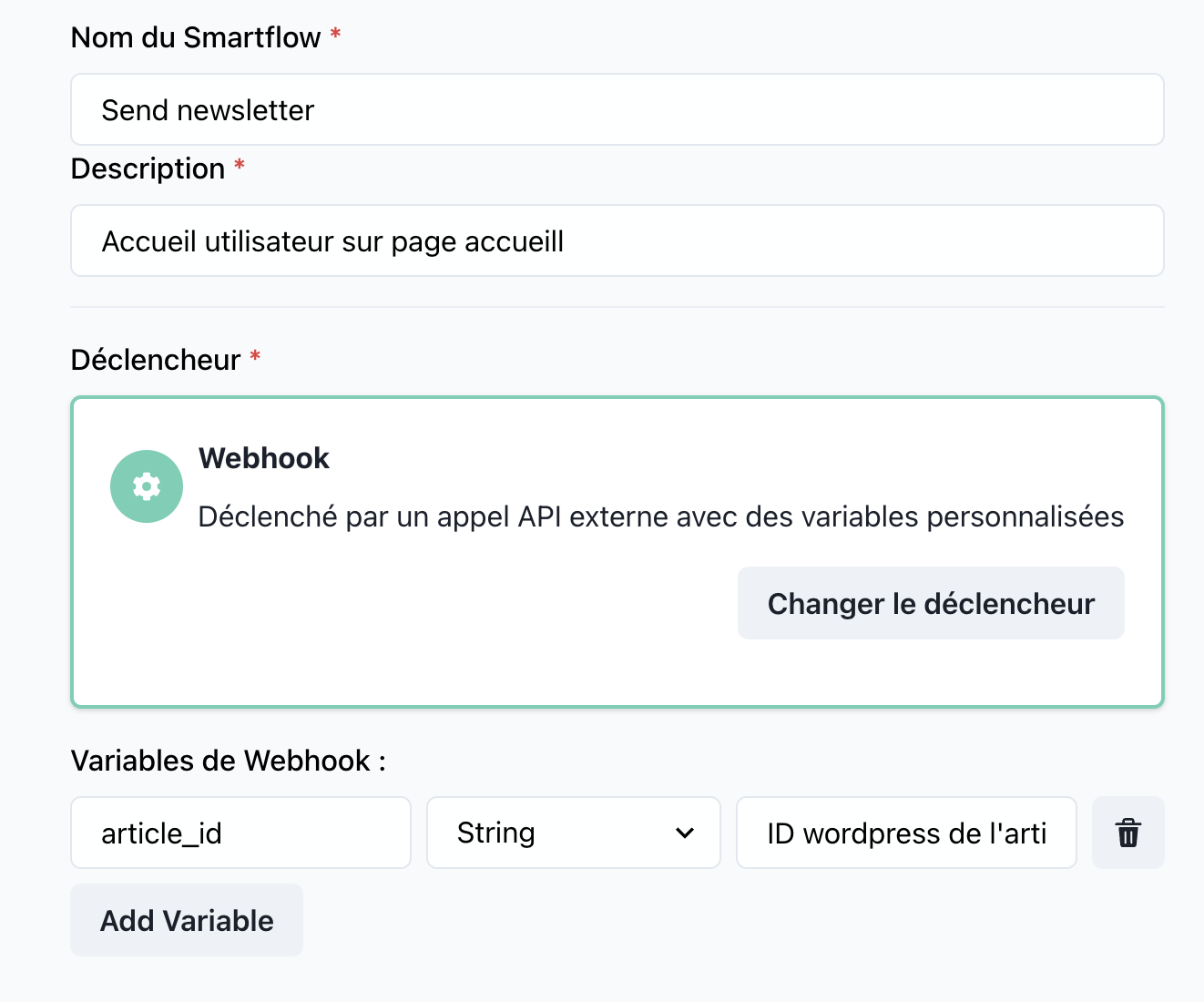
📝 Trigger Details
Name: Webhook
Category: Triggers
🔧 Parameters
1. Webhook URL
- Type:
string - Description: The endpoint URL for the webhook to receive incoming requests. This is automatically generated for each workflow using this trigger.
- Required: Yes
- Example:
https://api.smartflow.com/webhooks/{workflowId}
2. Payload
- Type:
object - Description: The data sent by the external system in the request body. This payload can include custom fields depending on the integration.
- Required: Yes
- Example:
{
"event": "order_created",
"orderId": "12345",
"customer": {
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john@example.com"
}
}
3. Headers
- Type:
object - Description: Optional headers that the external system might include for authentication or metadata purposes.
- Required: No
- Example:
{
"Authorization": "Bearer your-api-key",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
🚀 How It Works
-
Webhook URL Configuration:
- When creating a workflow with a Webhook Trigger, SmartFlow generates a unique URL for the webhook.
- Share this URL with the external system to configure their integration.
-
API Key Retrieval:
- Navigate to ChatModel Settings.
- Go to Integration → Web.
- Click Copy API Key to retrieve the necessary authentication token.
-
Payload Structure:
- External systems send data (payload) to the webhook URL using an HTTP
POSTrequest. - The payload must match the structure required by the workflow.
- External systems send data (payload) to the webhook URL using an HTTP
-
Trigger Execution:
- When the webhook receives a valid request, the associated workflow is triggered automatically.
- SmartFlow processes the payload, executes defined actions, and returns a response if necessary.
💡 Use Cases
-
CRM Integration:
- Scenario: A customer creates a new account in your CRM system.
- Webhook: The CRM sends a
POSTrequest to SmartFlow with customer details. - Workflow: Sends a welcome email and adds the customer to your marketing list.
-
Order Management:
- Scenario: An e-commerce platform processes a new order.
- Webhook: The platform sends order details to SmartFlow.
- Workflow: Updates inventory, sends an order confirmation email, and notifies the warehouse.
-
Incident Monitoring:
- Scenario: A monitoring system detects a critical error.
- Webhook: The system sends an alert to SmartFlow.
- Workflow: Creates an incident report and notifies the engineering team.
🔍 Example Configuration
Incoming Webhook Request
URL:
https://api.smartflow.com/webhooks/abc123
Payload:
{
"event": "user_registered",
"userId": "67890",
"name": "Jane Doe",
"email": "jane@example.com"
}
Headers:
{
"Authorization": "Bearer 123456789",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
🛠️ Best Practices
-
Validation:
- Validate incoming requests to ensure data integrity and prevent misuse.
- Use secure headers or tokens for authentication.
-
API Key Security:
- Ensure the API key retrieved from ChatModel Settings → Integration → Web is kept secure and not exposed publicly.
-
Data Mapping:
- Clearly map incoming fields to workflow variables for seamless processing.
-
Testing:
- Test the webhook with sample payloads to ensure compatibility and reliability.
-
Error Handling:
- Configure workflows to handle missing or malformed data gracefully.
📊 Monitoring and Debugging
-
Activity Logs:
Track incoming webhook requests and their processing status in SmartFlow’s dashboard. -
Error Reporting:
Identify failed requests and view error details for troubleshooting.
This section provides a detailed guide for the Webhook Trigger, ensuring users can integrate it seamlessly into their workflows. Let me know if you need any refinements!